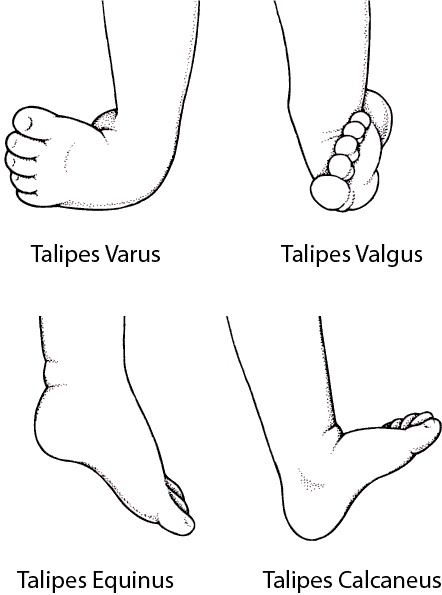
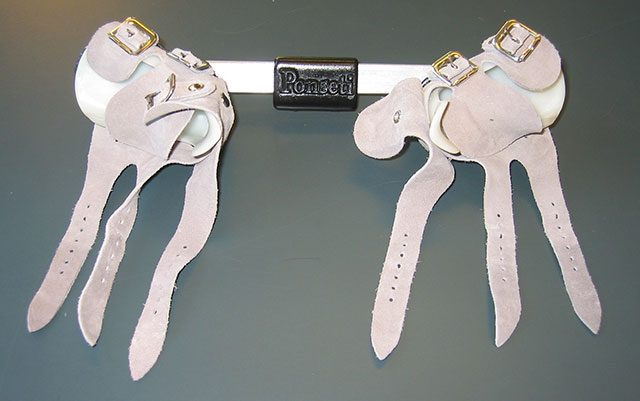
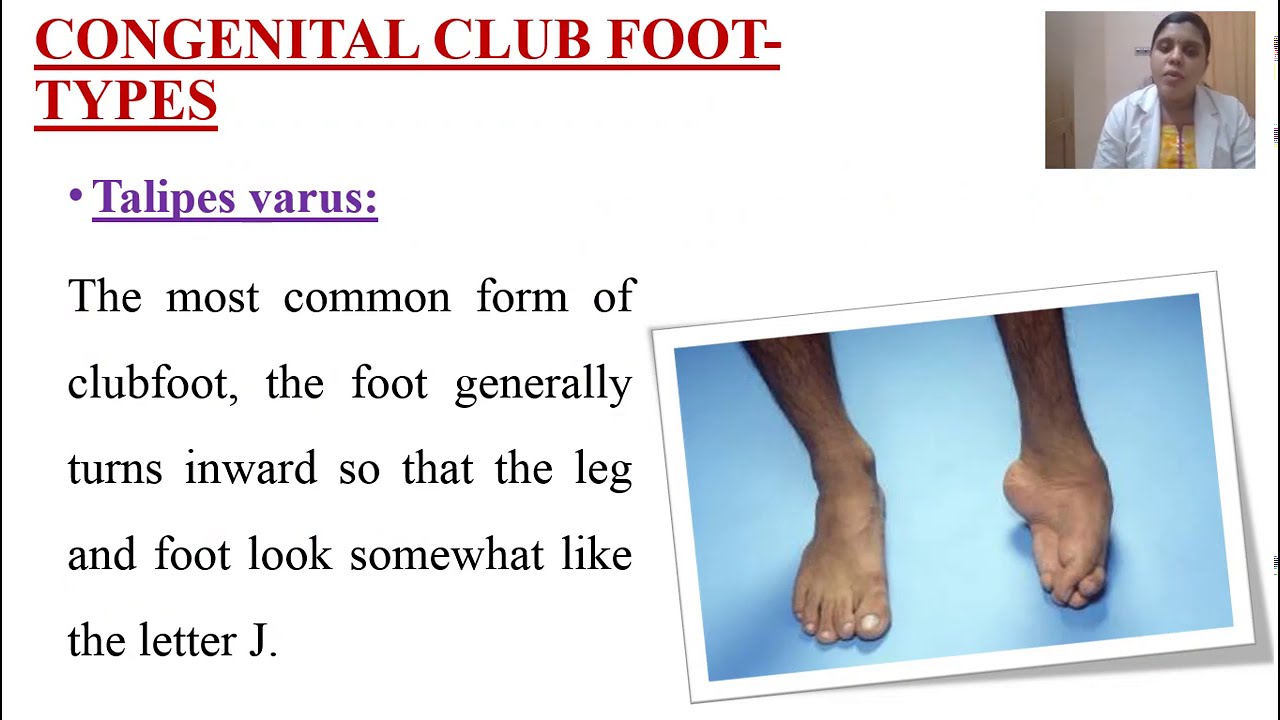
There are four variations of clubfoot talipes varus, talipes valgus, talipes equines, and talipes calcaneus In talipes varus, the most common form of clubfoot, the foot generally turns inward so that the leg and foot look somewhat like the letter J (when looking at the left foot headon) In talipes valgus, the foot rotates outward like the letter L CLUB FOOT Types Idiopathic (Unknown Etiology) CongenitalTalipes EquinoVarus CTEV Acquired, Secondary to CNS Disease Spina bifida, Poliomyelitis Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita Absent Bone fibula / tibia 10 CTEV MOST COMMON CONGENITAL FOOT DISORDER MALES 1/1000 LIVES BIRTHS 11Clubfoot braces, called Ponseti AFO's, consist of two shoes connected by a bar Both feet are braced, even if the clubfoot is only on one side The AFOs are positioned outward If there is a single clubfoot, that AFO will be turned outward more than the unaffected foot The brace is used full time (except for bath time) for three to four months
Clubfoot For Parents Nemours Kidshealth
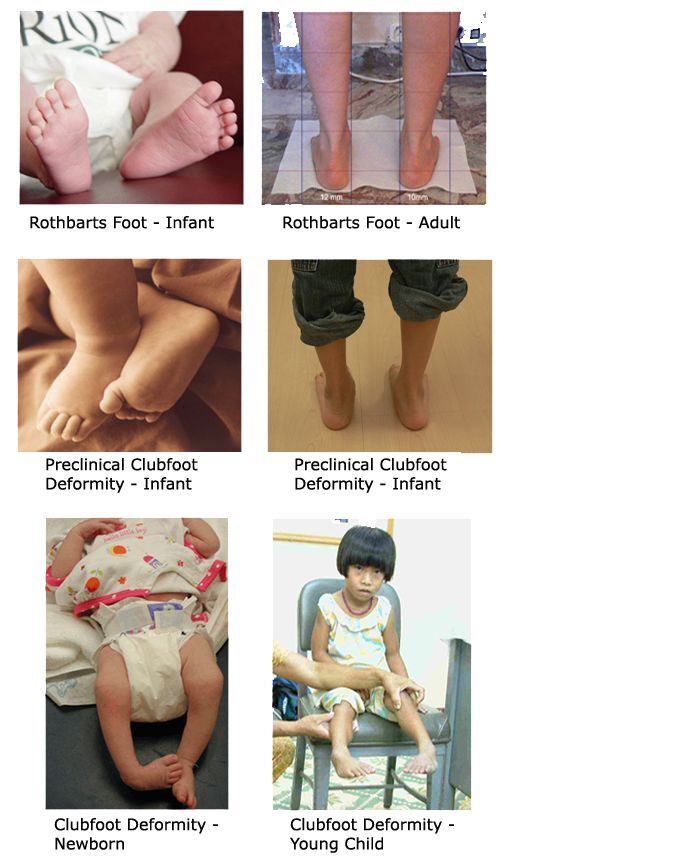
Club foot types
Club foot types- Adducted thumbclubfoot syndrome is characterized by typical facial appearance, slight build, thin and translucent skin, severely adducted thumbs, arachnodactyly, clubfeet, joint instability, facial clefting, and coagulopathy, as well as heart, kidney, or intestinal defects A clubfoot occurs when tight tendons and ligaments prevent the foot from stretching into the right position To repair a clubfoot, 1 or 2 cuts are made in the skin, most often on the back of the foot and around the inside part of the foot Your child's surgeon may make the tendons around the foot longer or shorter



Introduction To Clubfoot Physiopedia
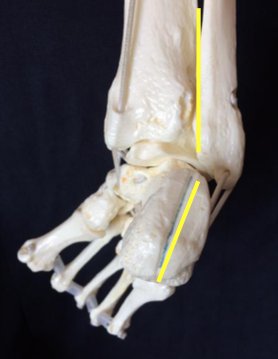
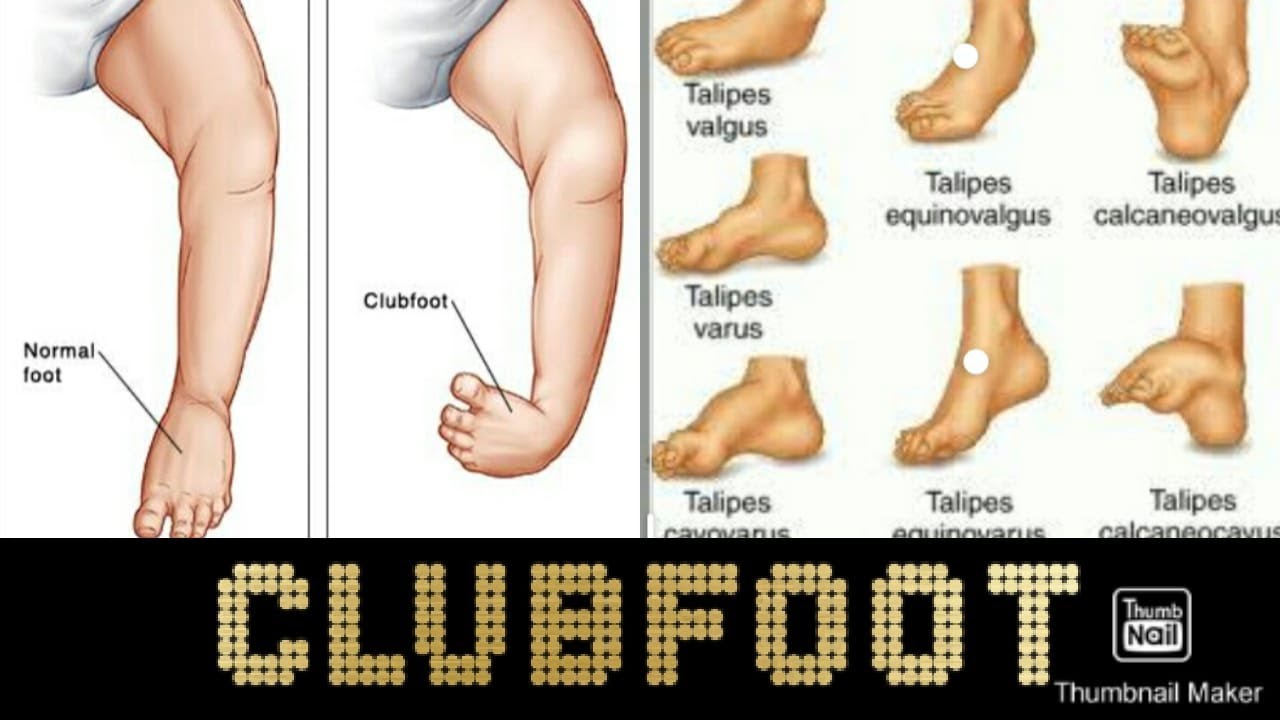
And talipes calcaneovarus (in which the ankle joint is dorsiflexed, and the forefoot deviated inwards)There are several types of clubfoot that are jointly known as 'talipes', as the deformity is mostly in the talus (a bone in the ankle) The most common of the talipes is what is known as "talipes equino varus" it is so common that the word clubfoot is commonly used to refer to this In talipes equino varus, the child is born with the foot pointing down and twisted inwards at the ankleTypes of clubfoot Clubfoot is often broadly classified into two major groups Isolated (idiopathic) clubfoot is the most common form of the deformity and occurs in children who have no other medical problems
Clubfoot is the only abnormality Positional This type of clubfoot occurs because the foot was in an abnormal position in the womb It is the easiest to treat Teratologic Clubfoot accompanied by other birth defects Clubfoot may be one sign of a general neuromuscular disorder (abnormalities of the nervous system or muscles) or part of aClubfoot, a very common congenital deformity, remained controversial regarding its nomenclature, etiology, pathoanatomy classification, management and prognosisA practical grading system, based only upon clinical assessments, has been tried on 1966 clubfeet The observations of over 29 years have endorsed this system as being quickly performed, adequately helpful in planning the11 reviews of Foot and Ankle Specialists of the MidAtlantic, LLC "I met with Dr David Vieweger, DPM and had a great experience The ladies at the front desk were friendly, the XRay tech was funny, and Dr Vieweger was very helpful His PA was a delight to work with as well I
Idiopathic clubfoot The most common type of clubfoot is idiopathic, which means the cause is unknown Idiopathic clubfoot is not related to any other medical problems Feet of babies with this type of clubfoot are stiff and hard to manipulate Syndromic clubfoot Syndromic clubfoot occurs when the condition is part of a larger syndrome This type is usually more severe and difficult to Congenital club foot in the human fetus A histological study J Bone Joint Surg Am 1980 Jan 62 (1)2 Scher DM The Ponseti method for treatment of congenital club foot Curr Opin Pediatr 06 Feb 18 (1)225 Hussain FN The role of the Pirani scoring system in the management of club foot by the Ponseti method Be sure to differentiate TEV from other types of "clubfoot", such as talipes calcaneovalgus, common in trisomy 18 (in which the ankle joint is dorsiflexed instead of plantar flexed, and the forefoot deviated outwards);



Clubfoot Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic




Club Foot 1
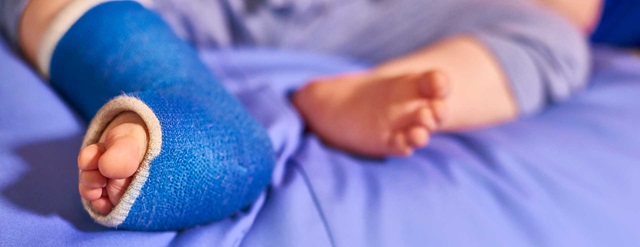
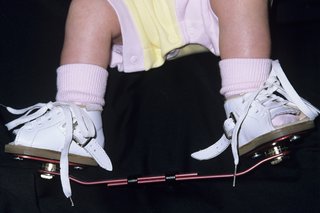
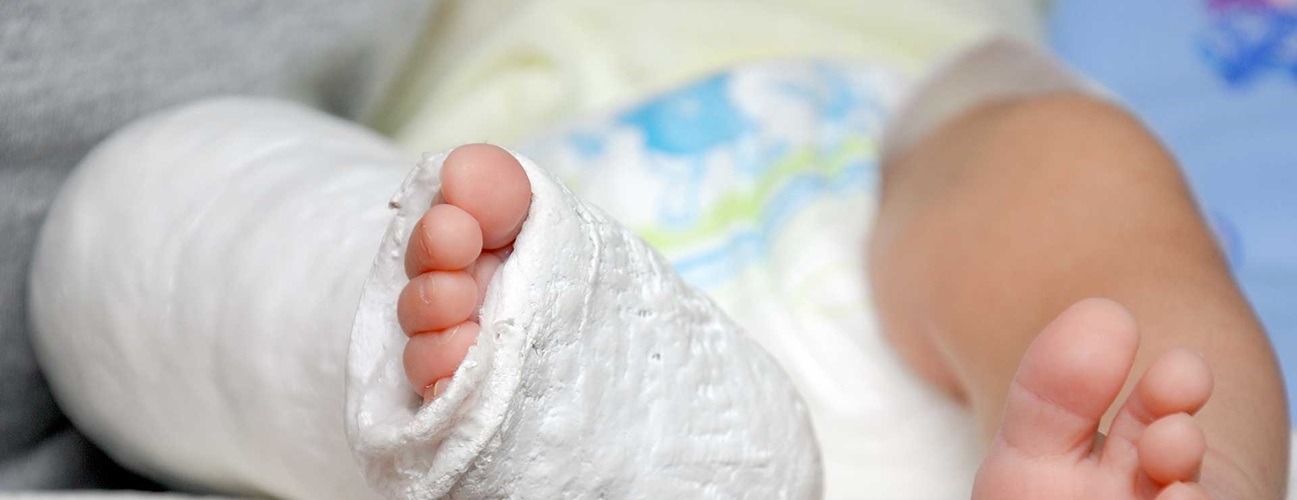
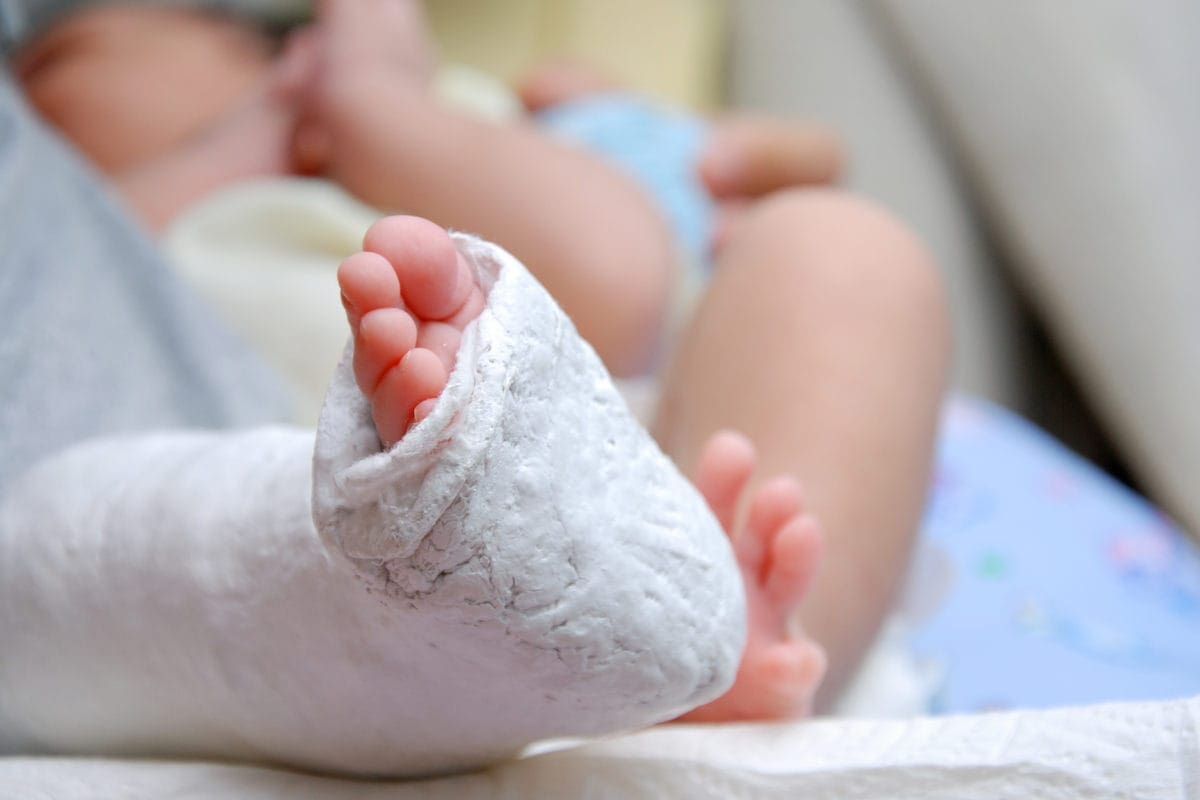
Casting for Club Foot Using the Ponseti method, the clubfoot is manipulated or stretched every five to seven days and the plaster casts are changedThis baby is on one of his last treatments for his clubfeet and will then wear a brace for a few years An alternative to serial casting is a specialized physical therapy treatment program, in which your child undergoes dailyClubfoot is a foot deformity classified into three different types idiopathic (unknown cause), neurogenic (caused by condition of the nervous system) and syndromic (related to an underlying syndrome) Idiopathic Clubfoot Also known as talipes equinovarus, idiopathic clubfoot is the most common type of clubfoot and is present at birthThis is a variation of the club foot, with a disk underneath an ovalshaped block of wood They are often at the base of cabriole legs and are indicative of Queen Anne furniture Spade Foot Popularized by Chippendale in the mid18th century, the spade foot is rectangular that is wide at the top and tapers to a narrow base




Honourable Ram Nath Kovind Inaugurates Global Clubfoot Conference Virily




Figure 2 From Correction Of Clubfoot Deformity Associated With Weber Type I Tibial Hemimelia Using The Ponseti Method Semantic Scholar
"Atypical" Clubfoot this is a type of clubfoot dealt with in the advanced section of this course (chapter 15) It involves a foot that is often swollen, has a plantarflexed first metatarsal and an extended big toe It can occur spontaneously but most often occurs after slippage of a castClubfoot is a foot malformation in which the foot is fixed in a plantarflexed position, and the sole is rotated inward The deformity may be unilateral or bilateral and affects the bony, muscular, and ligamentous structures Manual manipulation of the extremity does not correct the defectClubfoot (congenital talipes equinovarus) Clubfoot, also known as congenital talipes equinovarus, is a common idiopathic deformity of the foot that presents in neonates Diagnosis is made clinically with a resting equinovarus deformity of the foot Treatment is usually ponseti method casting



Clubfoot Johns Hopkins Medicine
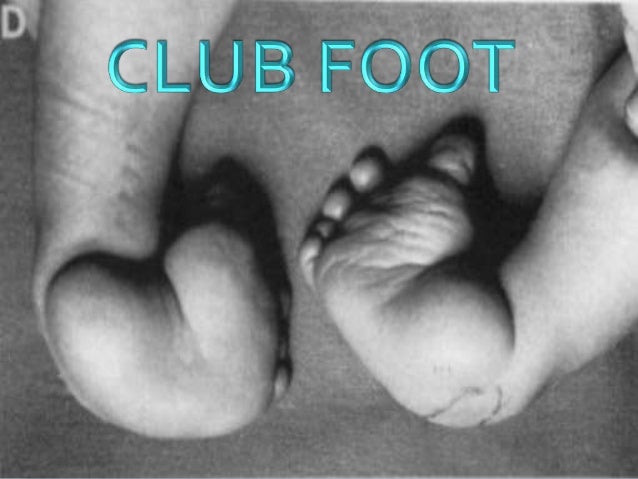



Club Foot
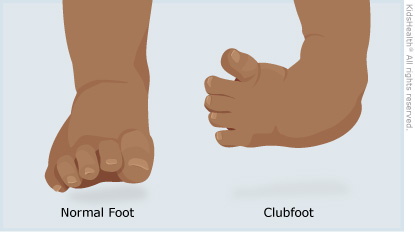
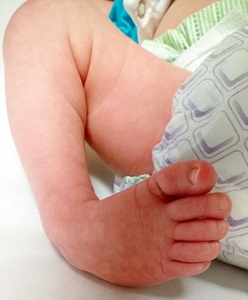
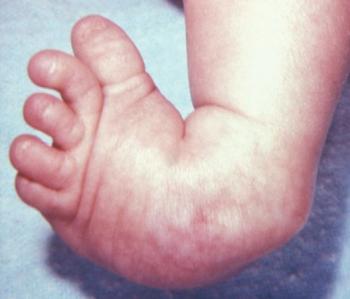
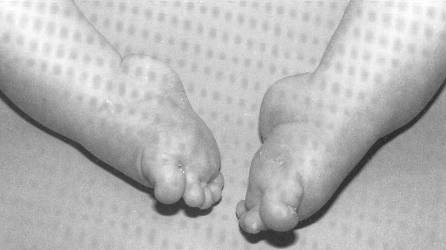
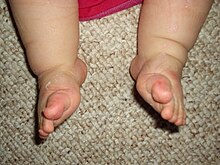
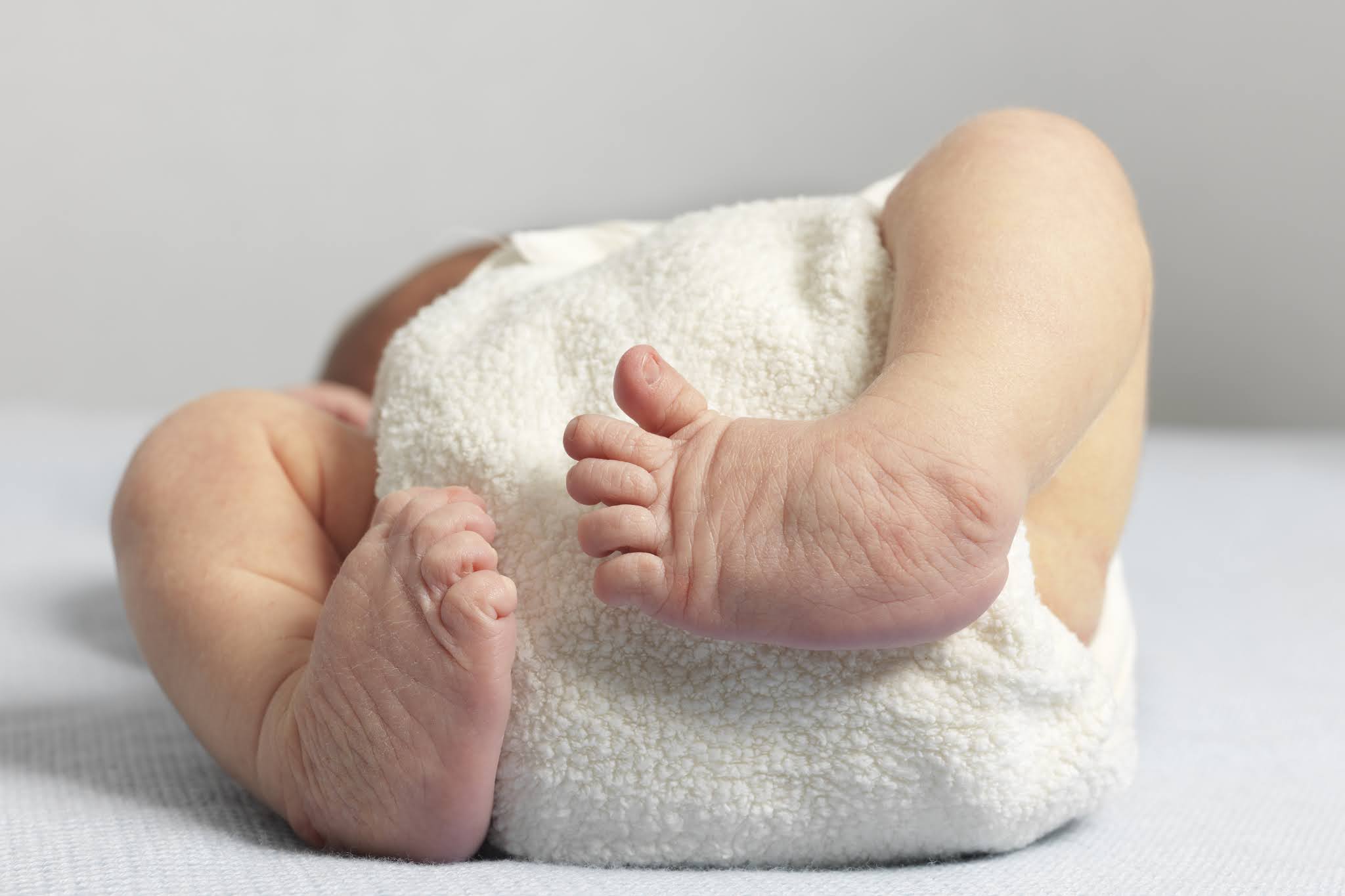
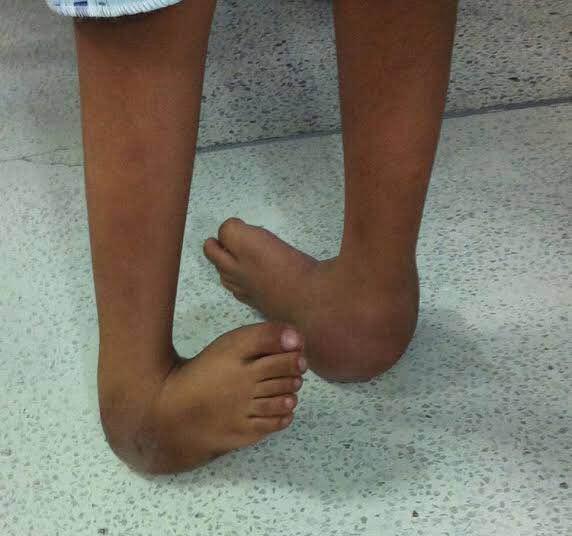
Achilles Tendon Lengthening If a child's clubfoot is resistant to treatment because the Achilles tendon doesn't stretch and grow as much as doctors expected after a percutaneous Achilles tenotomy was performed, doctors may recommend a procedure called Achilles tendon lengthening This procedure allows your child's foot to stretch and grow into the right position Appearance Clubfoot can range from mild to severe, but typically has the same general appearance The foot is turned inward and there is often a deep crease on the bottom of the foot (Left) A child with clubfoot in both feet (called bilateral) Clubfoot doesn't cause pain, but if it's not treated, it can make it hard for a child to walk without a limp It's easy to correct in most cases, so most children don't have longlasting
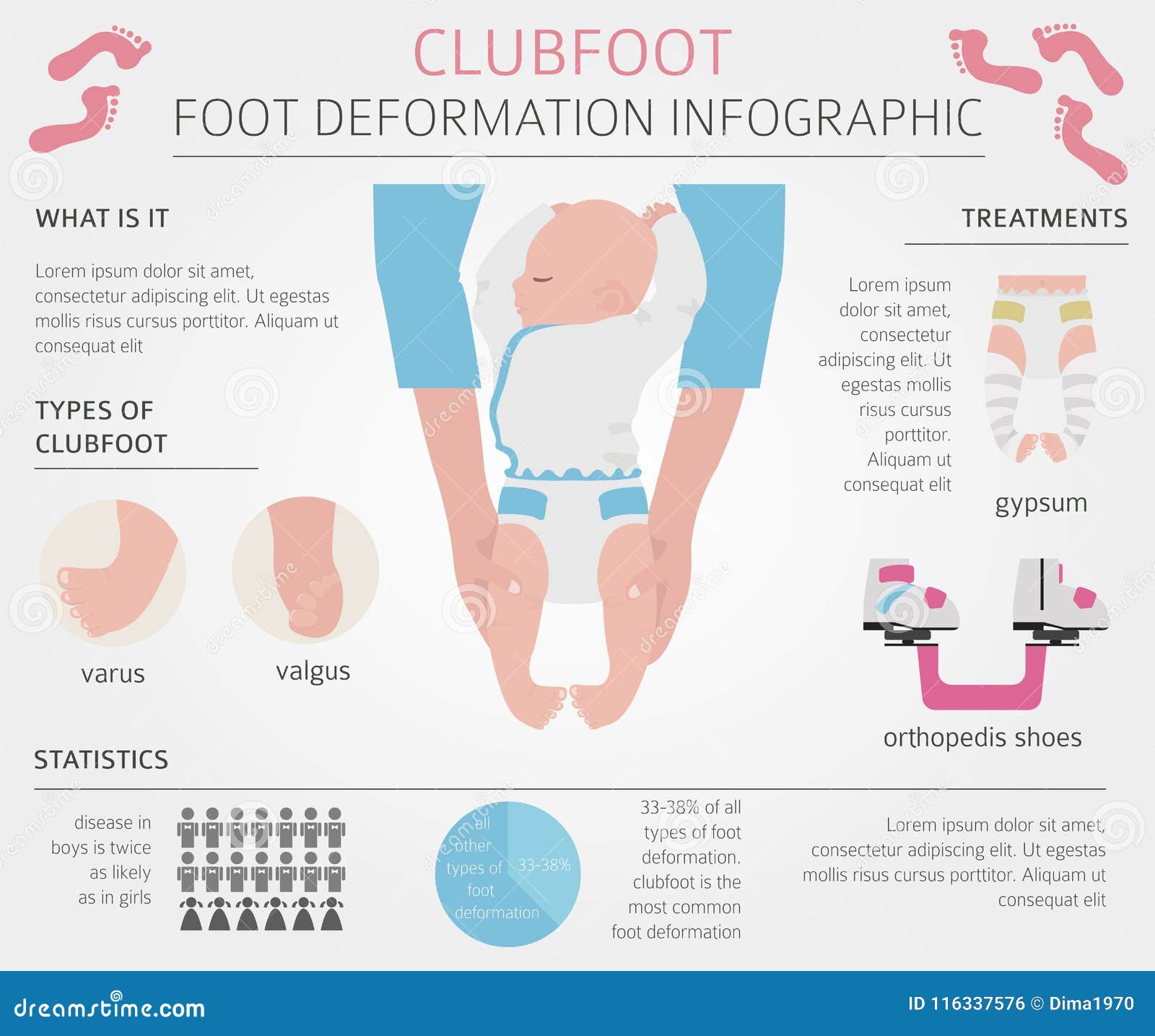



Clubfoot Stock Illustrations 98 Clubfoot Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Introduction To Clubfoot Physiopedia
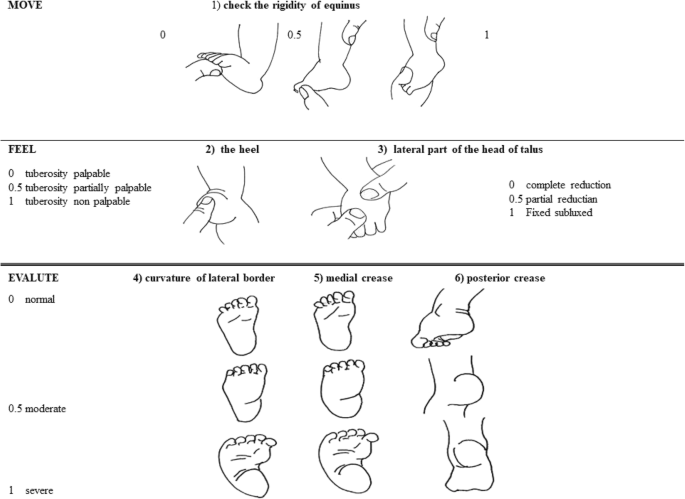
Congenital talipes equinovarus, or club foot, is one of the commonest congenital orthopaedic conditions Its incidence in the UK is approximatelyChildren who have clubfoot typically place weight on the side of their foot, rather than on the sole As a result, they develop painful calluses, weakened calf muscles and other complications However, most cases of clubfoot get treated before these types of problems developClubfeet must be classified according to severity to obtain reference points, assess the efficacy of orthopaedic treatment, and analyze the operative results objectively A scale of 0 was established on the basis of four essential parameters equinus in the sagittal plane, varus deviation in



Teaching Watercolor Of Clubfeet Onview Digital Collections Exhibits



Clubfoot Orthoinfo os
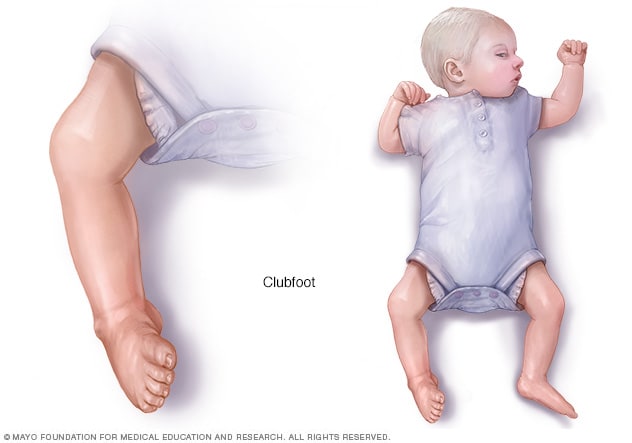
Clubfoot also can be discovered in utero (while the baby is still in the mother's womb) during an ultrasound An ultrasound is a type of imaging used to look at babies in the womb It is routine for a woman to have an ultrasound during her pregnancy to The term "clubfoot" refers to the way the foot is positioned at a sharp angle to the ankle, like the head of a golf club Despite its look, however, clubfoot itself doesn't cause any discomfort or pain 8 Infant with unilateral clubfoot Infant with bilateral clubfoot 9PDHonline Course S235 (1 PDH) Pole Foundation Design with Spreadsheet 12 Instructor John W Andrew, PE PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive




Clubfoot Wikipedia



Before Going To Doctor Which Must Know About Clubfoot Rxharun
Club foot (also called talipes) is where a baby is born with a foot or feet that turn in and under Early treatment should correct it In club foot, 1 foot or both feet point down and inwards with the sole of the foot facing backwards Credit Club foot happens because the Achilles tendon (the large tendon at the back of the ankle) is too shortThis video explain the etiology, clinical presentation, incidence, types and management of clubfoot It provides excellent overview for this condition and heExtrinsic This type is usually mild and supple The cause can be due to intrauterine compression (large baby, abnormally shaped or small uterus, or abnormal intrauterine fluid levels) Intrinsic This type is commonly more severe, rigid and the calf muscle is smaller The foot may be smaller and there can be a bone deformity of the talus




Clubfoot Boston Children S Hospital




Table 1 From Current Conservative Management And Classification Of Club Foot A Review Semantic Scholar
Clubfoot, also called talipes equinovarus, is a birth defect that affects the foot and ankle It's a congenital condition, which means that a baby is born with it The foot or feet turn inward When you look at the foot, the bottom of the foot often faces sideways or even up Clubfoot happens because of a problem with the tendons, the tissues 10 The NHS says "Club foot affects about 1 baby in every 1,000 born in the UK Both feet are affected in about half of these babies It's more common in boys" Club foot is usually diagnosed at birth, but it is possible to spot it during an ultrasound scan inStill, studies have reported clubfoot recurrence rates as high as 40% with the Ponseti method 3 Although research has shown the severity or type of clubfoot deformity can cause recurrence, many studies have highlighted that the strongest predictor of recurrence with the Ponseti method is nonadherence to bracing




Clubfoot Wikipedia




Foot Deformities Knowledge Amboss
Pediatric Clubbed Foot Clubfoot, also known as talipes equinovarus, is a congenital (present at birth) foot deformity It affects the bones, muscles, tendons and blood vessels and can affect one or both feet The foot is usually short and broad in appearance and the heel points downward while the front half of the foot (forefoot) turns inwardCongenital clubfoot is differentiated by structural, postural and secondary type The postural clubfoot can occur by abnormal position during birth and manipulative control The patient should be thoroughly examined to assess the features of paralytic clubfoot Congenital clubfoot can be rectifying completely Diagnostic tests Table 1 Pirani scoringEach type of clubfoot has unique characteristics and may need specific treatment Early recognition of the type of clubfoot one is dealing with can help guide appropriate treatment Individuals with clubfoot experience bone and soft tissues deformation and this abnormality can be presented through a range of abnormal alignments
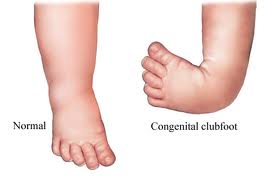



Introduction To Clubfoot Physiopedia



Clubfoot Symptoms Stages Definition Description Demographics Causes And Symptoms Diagnosis
Clubfoot is a foot deformity classified into three different types idiopathic (unknown cause), neurogenic (caused by condition of the nervous system) and syndromic (related to an underlying syndrome) Treatment for club foot usually starts within a Patients with osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or a severe injury may require this type of foot surgery Foot Surgeons in Central Maryland Our foot and ankle specialists at the Orthopaedic Associates of Central Maryland are boardcertified and fellowshiptrained to treat the full range of foot and ankle problems



Clubfoot Johns Hopkins Medicine




Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Narayana Health




A Summary Of The Clubfoot Assessment Protocol Cap Download Table




Clubfoot Talipes Equinovarus Symptoms Diagnosis And Treatment



Clubfoot Causes And Treatments




Clubfoot Wiki Thereaderwiki




Congenital Clubfoot Genetic Disorders Types Of Clubfoot




Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Narayana Health




Club Foot Talipes In Babies Causes Signs Treatment Youtube
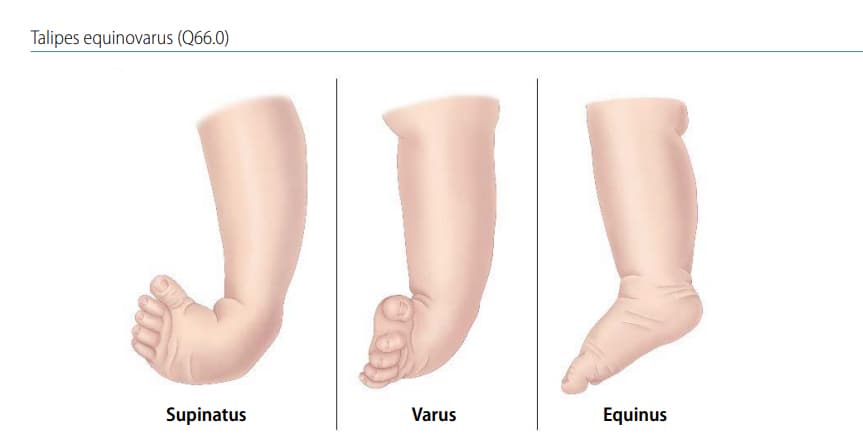



Chapter 4 9 Talipes Equinovarus Talipes Equinovarus Q66 0 Cdc




Congenital Talipes Equino Varus Congenital Clubfoot Ppt Video Online Download




Flatfoot Pes Planus Treatment Symptoms Shoes



Clubfoot Orthoinfo os



Club Foot Talipes Equinovarus Ankle Foot And Orthotic Centre




Greatly Blessed Clubfoot Basics Life With An Afo Club Foot Baby China Adoption Club Foot




Recognize The Types And Methods Of Handling Club Foot In Infants Or Club Foot Window Of World
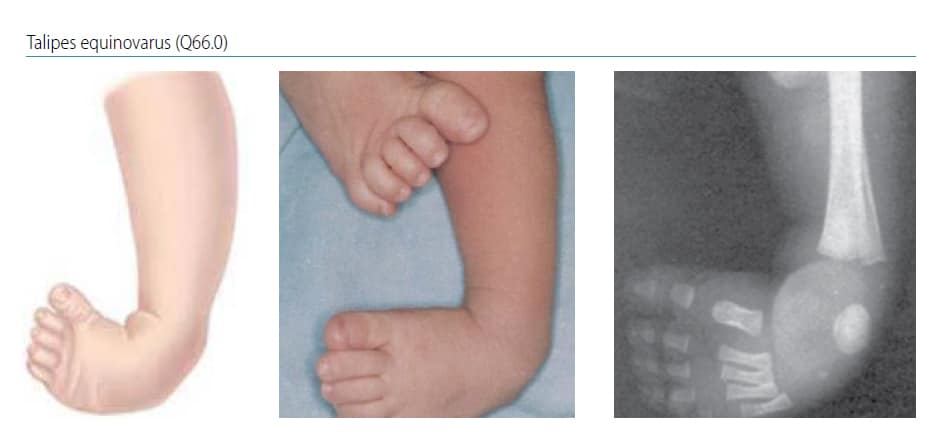



Chapter 4 9 Talipes Equinovarus Talipes Equinovarus Q66 0 Cdc



Clubfoot Causes And Treatments




To Parents Of Children Born With Clubfeet University Of Iowa Stead Family Children S Hospital



Clubfoot Talipes Equinovarus Tev Youtube




Osteogenesis Imperfecta And Clubfoot A Rare Combination Case Report And Review Of The Literature Abstract Europe Pmc



Clubfoot Congenital Equinovarus Cev Team Bone




Clubfoot Wikipedia




To Parents Of Children Born With Clubfeet University Of Iowa Stead Family Children S Hospital



Club Foot Nhs




Clubfoot Wikipedia




4 1 Clubfoot Types Clubfoot Guide 123



Clubfoot And Other Foot Defects Children S Health Issues Merck Manuals Consumer Version




Clubfoot Artemisia Panou Md Phd




Clubfoot Repair Treatments Procedure Outlook




Pdf Current Conservative Management And Classification Of Club Foot A Review Semantic Scholar




Easing Concerns About Clubfoot Wheat Ridge Co Granby Co Rocky Mountain Foot Ankle Center




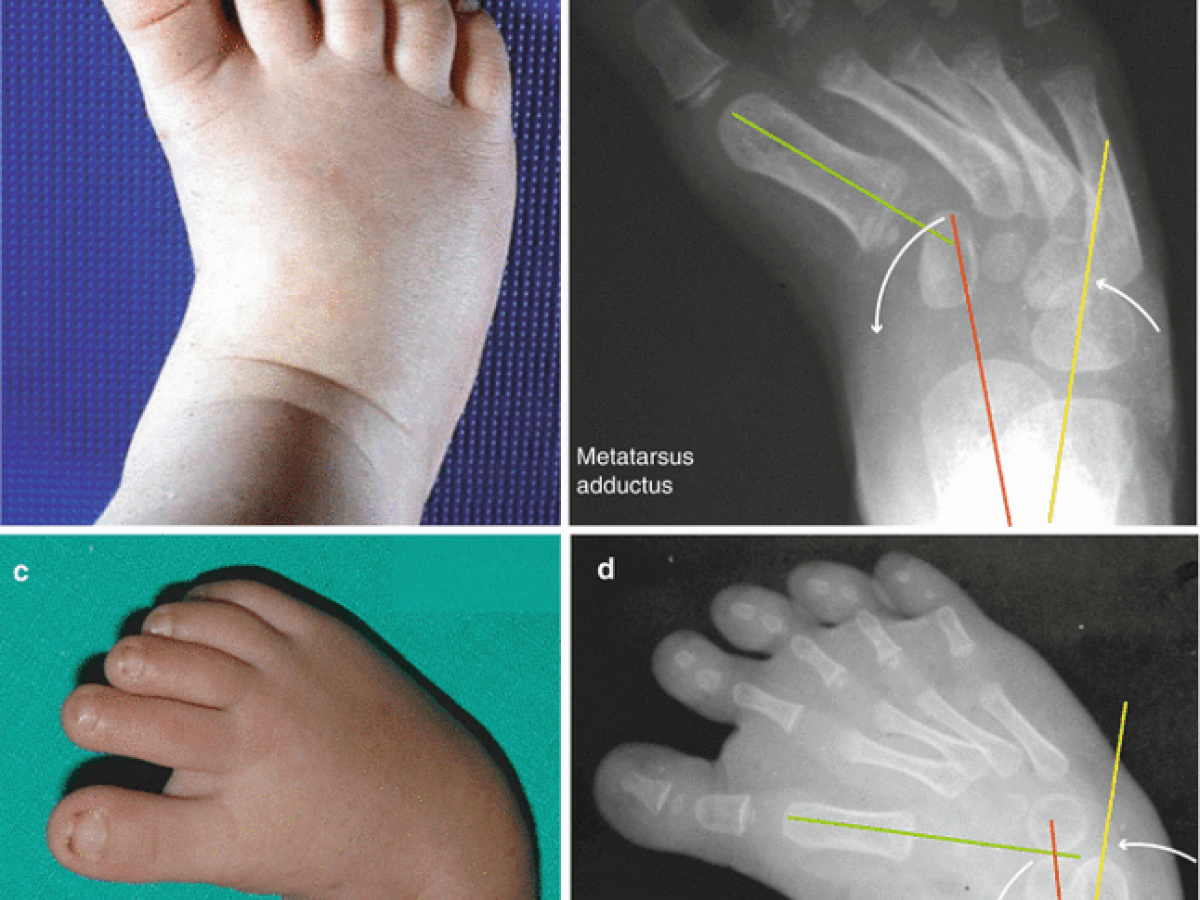
Metatarsus Adductus Johns Hopkins Medicine



Clubfoot Orthoinfo os




Clubfoot Boston Children S Hospital




Prevalence And Characteristics Of Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Clubfoot In Northern Ghana A Two Year Retrospective Descriptive Study African Journal Of Current Medical Research




Clubfoot For Parents Nemours Kidshealth




Foot Deformation Medical Desease Infographic Clubfoot Defect Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock




Clubfoot Causes Symptoms And Diagnosis




Clubfoot Johns Hopkins Medicine




Clubfoot Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Rigidfeet Instagram Posts Gramho Com




32 Clubfoot Ideas Club Foot Club Foot Baby Pediatric Physical Therapy



3 Embryological Foot Types Athlepedia The Athletics Wiki Fandom




Club Foot



Clubfoot Wikipedia




Club Foot



1




Foot Deformities Various Talipes Conditions Pediatric Physical Therapy Pediatric Nursing Medical Terms




Congenital Talipes Equino Varus Congenital Clubfoot Ppt Video Online Download




Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Narayana Health



Clubfoot Orthoinfo os




Clubfoot And Its Treatment Dr Michael Vohrer




Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Clubfoot Nursing Care Management Pediatric Physical Therapy Medical Dictionary Medical Anatomy




Clinical Photographs Showing A The Club Feet Of A 1 5 Month Old Baby Download Scientific Diagram




How To Treat Club Foot Causes Symptoms And Treatments Herapedia




Congenital Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equino Varus Ppt Video Online Download



About 100 000 Nigerians Suffer Clubfoot Yearly Noa




By Cassie Maier What Is Club Foot Club Foot Is When One Or Both Babies Feet Are Turned Inward And Downward And Cannot Be Put Into Normal Position Easily Ppt Download



1




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader




Club Foot Symptoms And Treatment
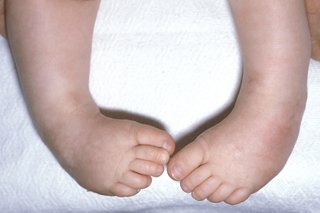



Club Foot Nhs
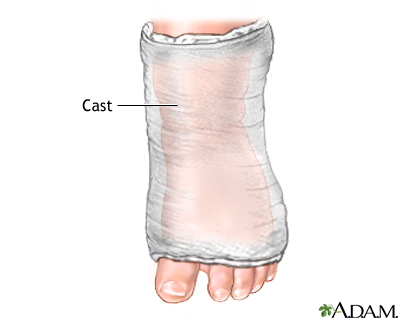



Clubfoot Repair Series Procedure Part 1 Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia
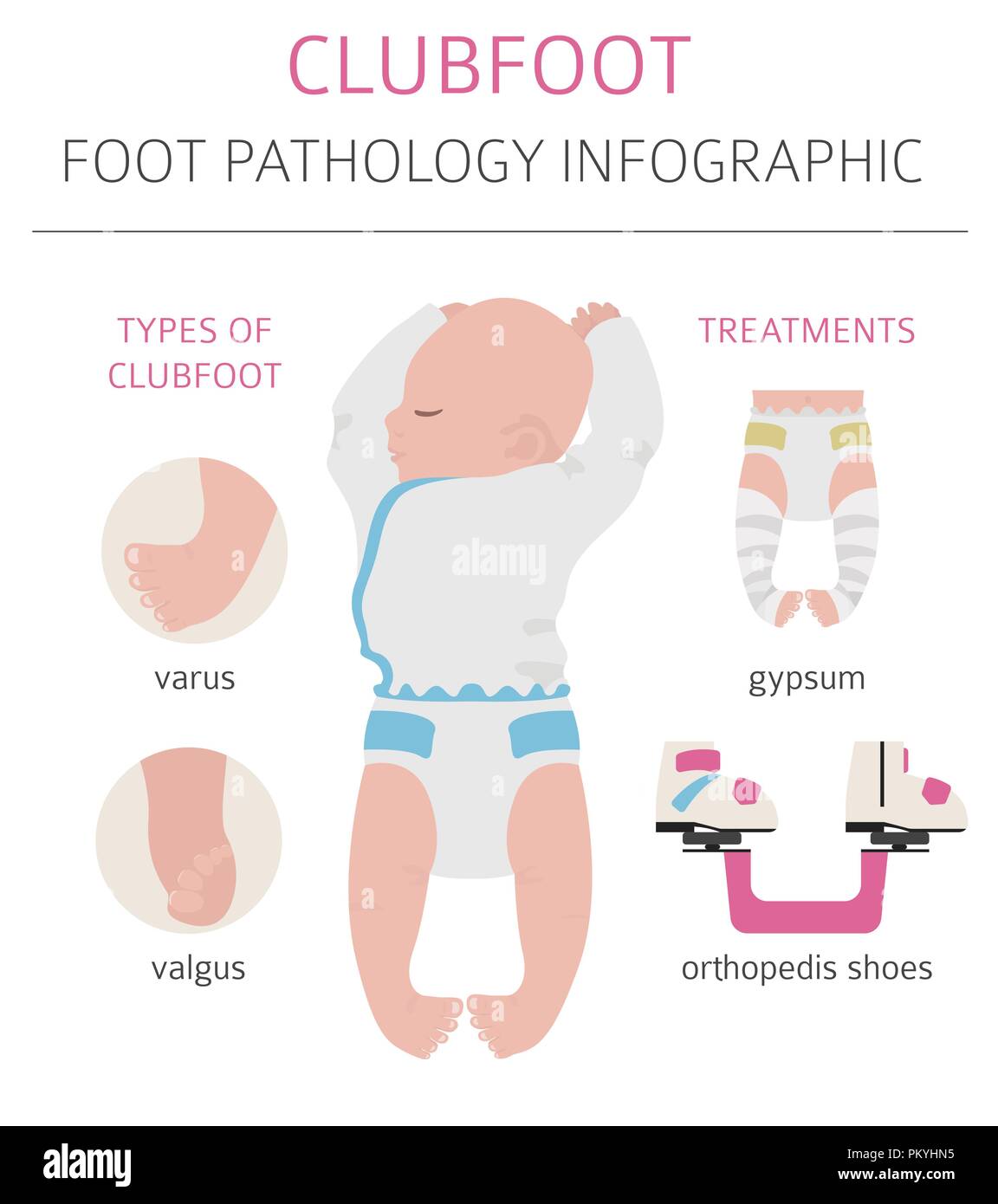



Clubfoot High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy



Clubbed Foot Berel
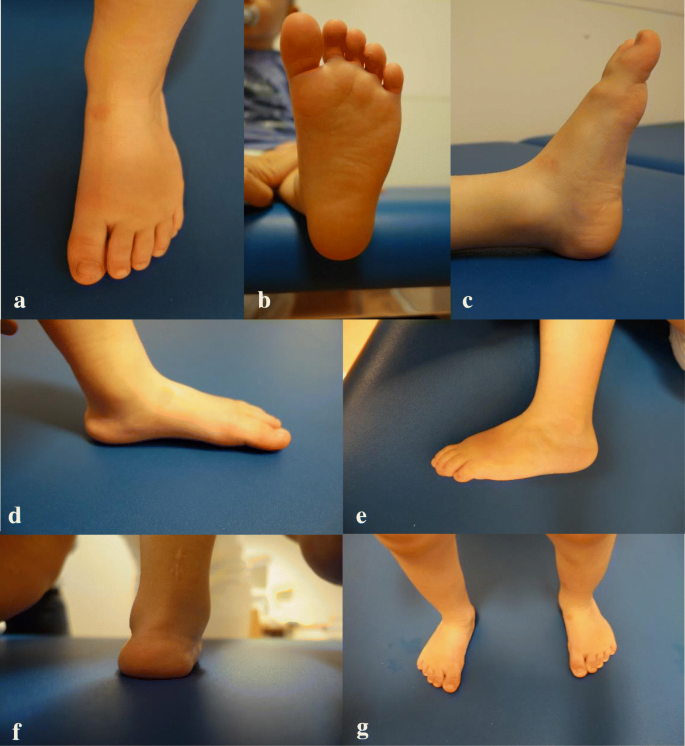



Is Unilateral Lower Leg Orthosis With A Circular Foot Unit In The Treatment Of Idiopathic Clubfeet A Reasonable Bracing Alternative In The Ponseti Method Five Year Results Of A Supraregional Paediatric Orthopaedic Centre



What A Paediatrician Should Know About Congenital Clubfoot Italian Journal Of Pediatrics Full Text



Congenital Club Foot In Child Kerala Nurses Hub Youtube




Idiopathic Talipes Equinovarus Congenital Clubfoot Disclaimer The Findings



1



Clubfoot Its Types And Causes Simplified In Hindi Youtube



Common Foot Problems In Children Foot And Ankle



1



Clubfoot Orthoinfo os
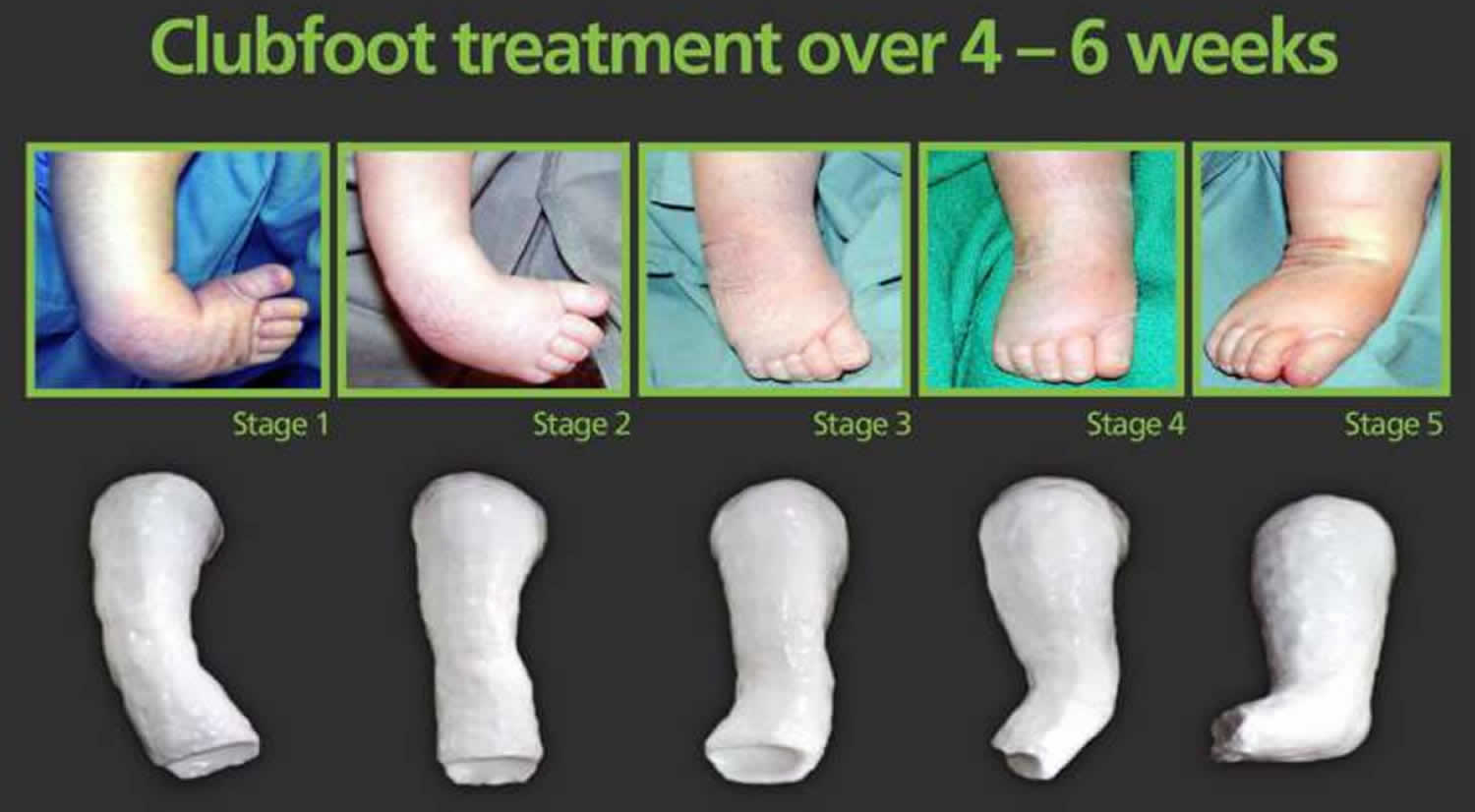



Ponseti Method For Clubfoot Treatment
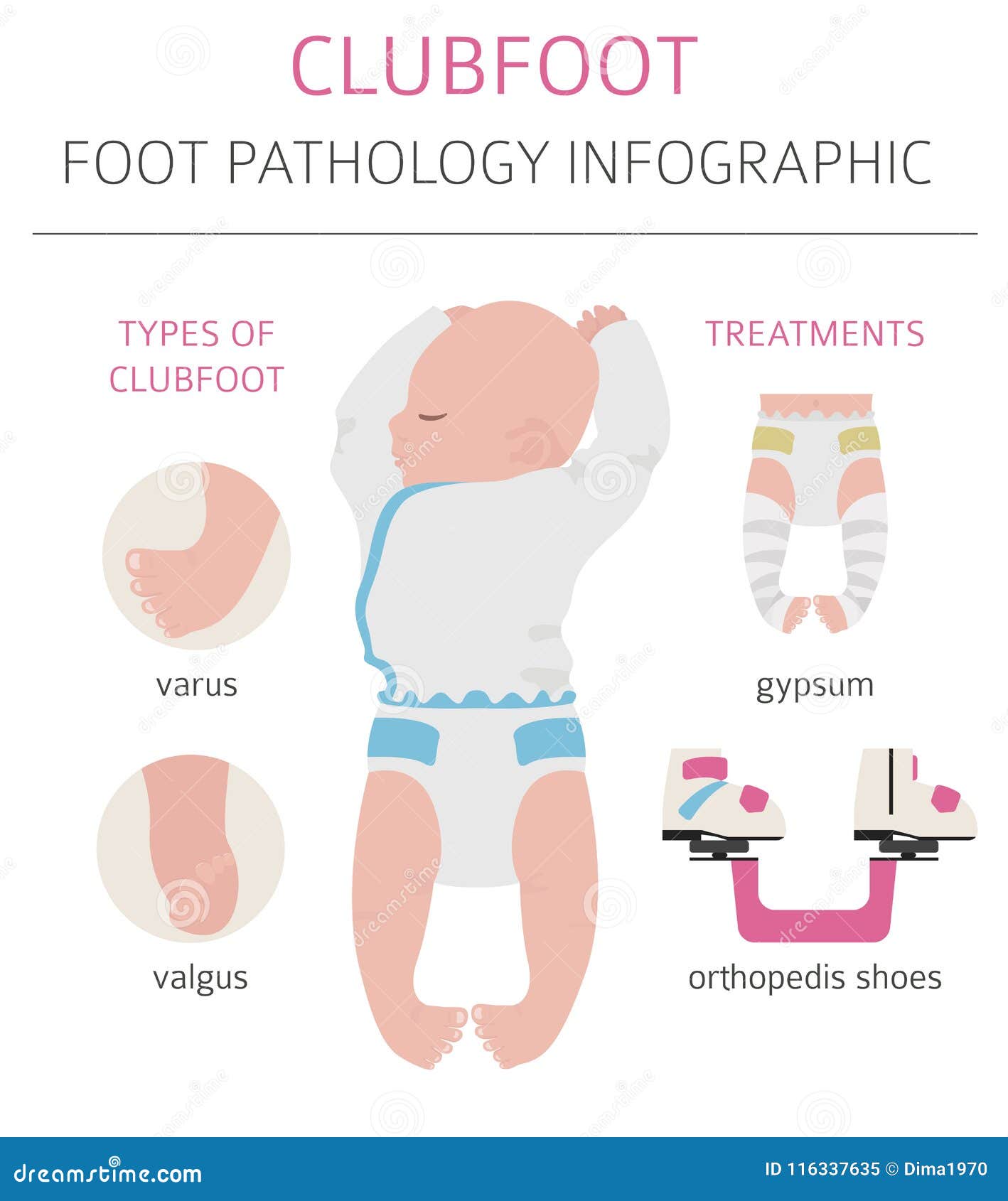



Foot Deformation Medical Desease Infographic Clubfoot Defect Stock Vector Illustration Of Condition Alignment




Clubfoot Nurse Key
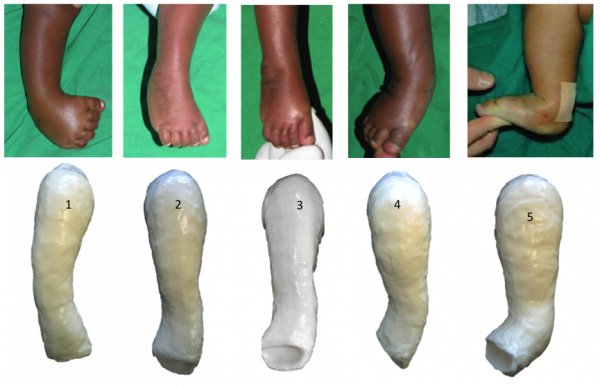



Ponseti Method Physiopedia



Introduction To Clubfoot Physiopedia
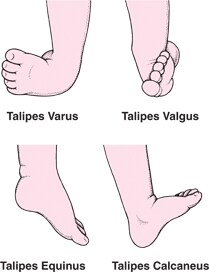



Clubfoot And Other Foot Defects Children S Health Issues Medicine Com




What Is Clubfoot Symptoms And Treatment Familydoctor Org



Clubfoot What Is Clubfoot What Causes Clubfoot Who Gets Clubfoot What Are The Symptoms Of Clubfoot




Congenital Talipes Equino Varus Congenital Clubfoot Dr Imran
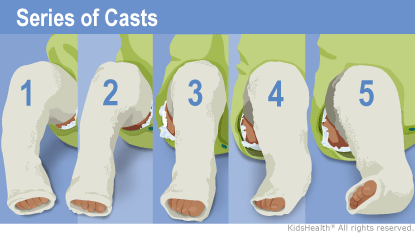



The Ponseti Method Casting Phase For Parents Nemours Kidshealth




Clubfoot Flip Ebook Pages 1 Anyflip Anyflip



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿